The ‘Everything-You-Need-to-Know’ Guide on Structured Trade Finance
According to recent reports, the global trade finance market is estimated to reach US$ 68.62 Bn by 2032. Undoubtedly, trade is the backbone of economies worldwide and is an important driver for development.
That said, in 2020, the global trade finance gap hit an all-time high of $1.7 trillion. The subsequent lockdowns and the reeling impact of the pandemic have only worsened the situation. There is a dire need to improve the current trade finance system, especially for small businesses that fuel global economic growth. Trade finance instruments play a significant role in the free movement of goods and commodities from one country to another. New technology interventions are needed to transform trade finance instruments into profitable capital market products and further enable easy access to affordable trade finance assets.

In this post, we take a look at what structured trade finance is, how it is different from conventional lending, how it strengthens the trade finance ecosystem, and more.
What is structured trade finance?
Structured Trade Finance (STF) is a type of debt finance that brings together trade finance products from across the supply chain.
Often used as an alternative to conventional lending, structured trade finance boosts bilateral transactions that involve high-value goods in large quantities.
In a structured trade finance transaction, the benefit to business owners is that they can source products even if they do not have the cash needed to purchase them from a supplier. The main objective of this financial instrument is to reduce the potential risks involved in international trade. It aims to enhance trade security and make lending as well as access to credit, more convenient for all stakeholders.
How does structured trade finance work?

Structured trade finance helps in reducing the gap between the buyer fulfilling a purchase order and the seller expecting the payment—either upfront or when the goods are shipped.
In a structured trade finance transaction, a trade financier helps a buyer purchase goods, either by making the payment to the seller or lending money to the buyer to seal the deal. The money borrowed, is then repaid through the production, storage, transfer, or sale of the goods.
It is a structured transaction where the proceeds of the sale are used to repay the loan offered by the trade financier. The loans are also tailor-made to suit the business cycle, region, and transaction.
Structured trade finance offers innovative trade solutions that reduce the risk involved in international trade transactions by providing a secure means of payment and delivery to traders, importers, buyers, sellers, and intermediaries.
Why opt for structured trade finance?

The primary objective of choosing structured trade finance solutions is to mitigate the risks involved in cross-border transactions. Such structures fortify the export-import business enabling diversification of funds, extending payment times, helping clients expand their facilities, and engaging in strategic procurement.
Another reason why structured trade finance is useful to businesses is that, as opposed to a standard loan, lenders do not stress the strength of the borrower. Instead, they look at the structure of the transaction, the trade cycle of the product, and the underlying cash flows before considering the business for a loan.
Why is structured trade finance important?
Some of the key benefits that structured trade finance offers are:
● Mitigates risk
It helps your business reduce potential risks that could arise from cross-border and cross-country transactions. Structured trade finance mitigates the risk considerably by using financial instruments such as letters of credit that guarantee payment and provide assurance to the seller that they will receive payment once the goods are shipped or delivered.
● Boosts cash flow
Structured trade finance improves your business cash flows by offering a reliable and secure means of payment. This financial instrument is particularly useful for smaller companies that are risk-averse.
● A robust financing structure
This trade finance instrument offers a custom-made financing structure tailored to the trade financing needs of your business.
● Fosters competitiveness in business
Structured trade finance will make your business more competitive by enabling you to step up your game, explore new markets and find new customers.
● Builds trust among stakeholders
It helps forge a strong bond between buyers and sellers building trust along the way. By creating a secure way to access credit and fulfil orders, structured trade finance builds trust and confidence in buyers and sellers to carry out large orders across borders.
How is structured trade finance different from conventional lending?
In conventional lending banks and financial institutions offer loans to approved businesses and the businesses repay the loan along with interest and any other fees that may apply over an agreed period of time.
Whereas in structured trade finance, multiple loans are provided at different stages of the supply chain. These loans are tailored according to the needs of the client and the loan is repaid based on the movement and sale of the goods.
Types of structured trade finance
Structured trade finance covers various modes of finance for traders and producers involved, such as:
● Pre-export finance

In pre-export finance, funds are provided to the exporter of the goods based on the confirmed orders from buyers.
In a typical pre-export finance transaction, the borrower uses the funds to meet working capital needs which include the purchase of raw materials and costs associated with storing and movement of goods. Usually, pre-export facilities finance 80% of the production.
● Borrowing base facilities

This is a type of structured trade finance, where the amount a borrower can obtain is determined by the value of a pool of current assets that the company is holding. The pool of assets can vary which means that the loan amount will vary accordingly, depending on the asset’s value.
● Warehouse financing
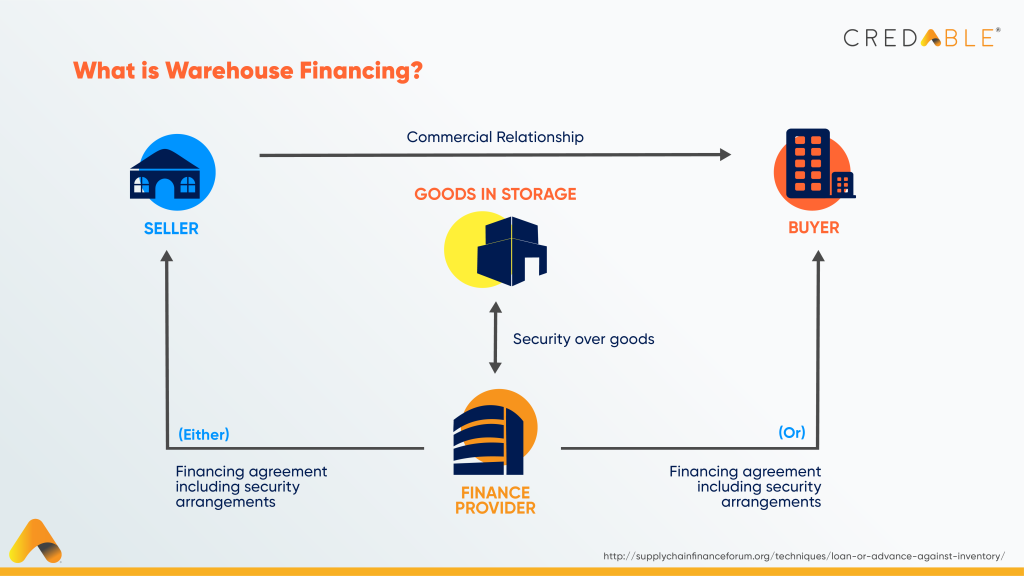
It is a type of inventory financing where a company or a manufacturer avails a loan from a financial institution by using their goods as collateral for the loan. The commodities are kept in a warehouse approved by the lending institution or managed by a third party. If the company fails to repay the loan or delays the payments, the lender can seize and sell the goods to recover the losses.
● Uncommitted trade facility
It is a term used to define an agreement between a borrower and a lender wherein the lender determines the amount that will be offered as a loan but is under no obligation to make it available. Small businesses often struggle with sufficient cash flows. An uncommitted trade facility will help businesses meet their immediate working capital needs as it is made available to them for a short duration.
● Receivables financing
This is a funding technique where a company receives funds based on its outstanding invoices. These invoices represent past orders for which payment is awaited. By selling its receivables, a business can obtain payments in advance, allowing it to invest in R&D, innovation, and business growth.
The takeaway
The role of Structured trade finance in trade business is only going to grow in the years to come. Such trade options are safe to rely on in times when trading activities are dropping. They are a huge boost to emerging economies and will continue to be in the future.
Today, CredAble is at the forefront of shaping the future of supply chain financing. CredAble offers scalable trade finance solutions right from the purchase order stage to the post-invoice acceptance stage, unlocking value for every participant in the ecosystem.
